The Science of Emotion: How Affective AI can Transform Psychological Experiments
Harnessing Multimodal Emotion AI to Support Children's Emotional Well-Being and Development
For decades, psychologists have studied human emotions through experiments that reveal patterns in behavior, decision-making, and emotional responses. Now, with modern technologies like Affective AI, emotion analysis has become more advanced than ever. This blog explores the role of psychological experiments, the importance of analyzing data from multiple sources like video, image, audio, and text, and how Affective AI enhances these studies for deeper insights.
Psychological Experiments: A Window into Human Emotion
Psychological experiments are structured studies designed to investigate human behavior, cognition, and emotion under controlled conditions. Classic studies, such as the Marshmallow Test and the Stanford Prison Experiment, have provided valuable insights into delayed gratification, social roles, and emotional resilience.
A critical aspect of these experiments is data collection and processing. Traditionally, psychologists rely on manual observation, surveys, and behavioral coding to analyze responses. However, with the advent of AI-driven tools, psychological research now benefits from more precise, scalable, and detailed emotion analysis.
The Importance of Data Processing in Psychological Experiments
Data in psychological experiments can be collected from various sources:
Video: Capturing facial expressions, body language, and micro-expressions.
Image: Analyzing still frames for nuanced emotional changes.
Audio: Assessing tone, pitch, and intensity of voice.
Text: Evaluating sentiment, word choices, and psychological markers.
Processing these data points accurately is essential for drawing meaningful conclusions. Advanced AI models now allow researchers to automate and refine these analyses, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of human emotions.
Affective AI: Decoding Emotions from Multiple Modalities
Affective AI, also known as Emotion AI, employs sophisticated AI/ML techniques to process and interpret human emotions. It analyzes data from video, image, audio, and text, mapping emotions with high accuracy. Here's how it works across different modalities:
Video Emotion Analysis: AI identifies facial expressions, micro-expressions, and changes in emotion throughout the duration of an experiment. It can track real-time shifts in mood and engagement levels.
Image Emotion Recognition: Using the Facial Action Coding System (FACS), AI deciphers facial movements associated with specific emotions, offering a static yet detailed emotional assessment.
Audio Emotion Analysis: AI processes voice pitch, tone, intensity, and rhythm to detect emotions such as happiness, surprise, and sadness.
Text Emotion Analysis: AI scans verbal expressions, social cues, and sentiment markers to understand the psychological and emotional context of responses.
By combining these modalities, Affective AI provides a multi-layered view of human emotions, offering deeper insights than traditional methods alone.
Bridging Psychological Experiments and Affective AI: The Marshmallow Test Revisited
A classic example of a psychological experiment that benefits from Affective AI is the Marshmallow Test. Designed by Walter Mischel in the late 1960s, the test evaluates a child's ability to delay gratification. Children are given a marshmallow and told they can either eat it immediately or wait to receive a second marshmallow. The test aims to measure self-control and its correlation with long-term success.
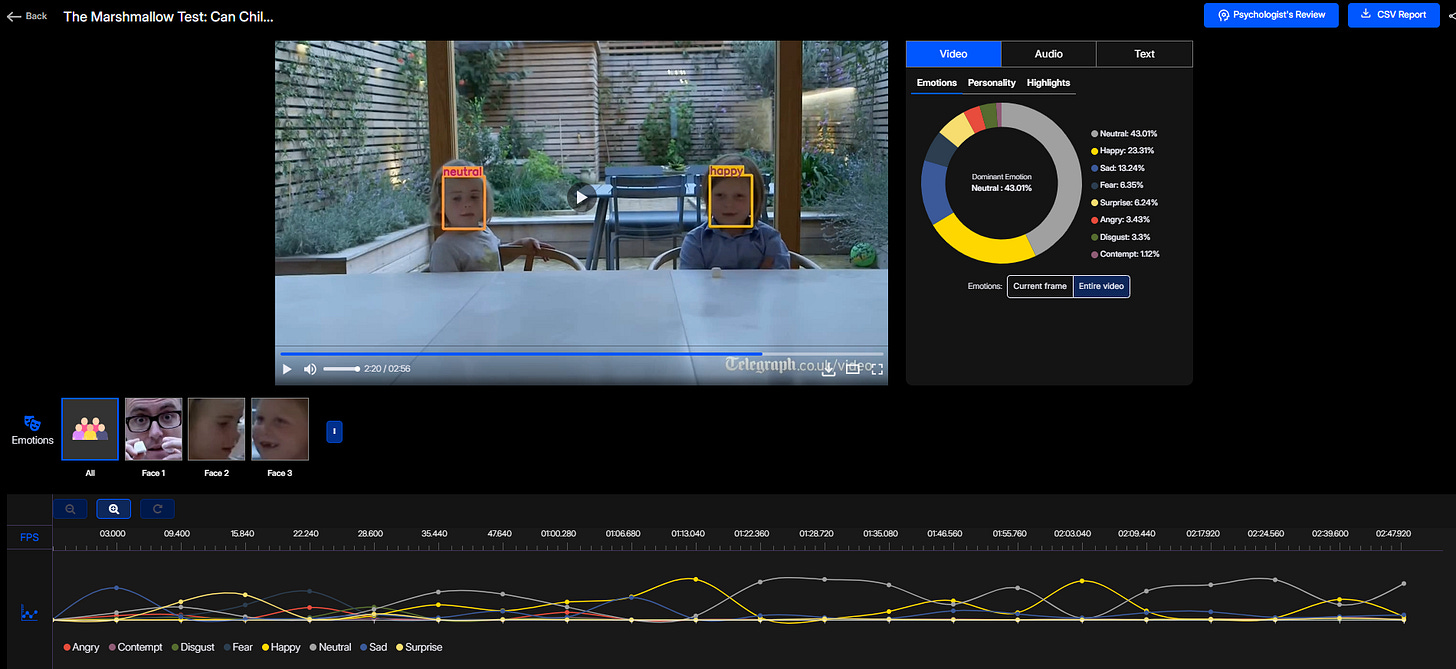
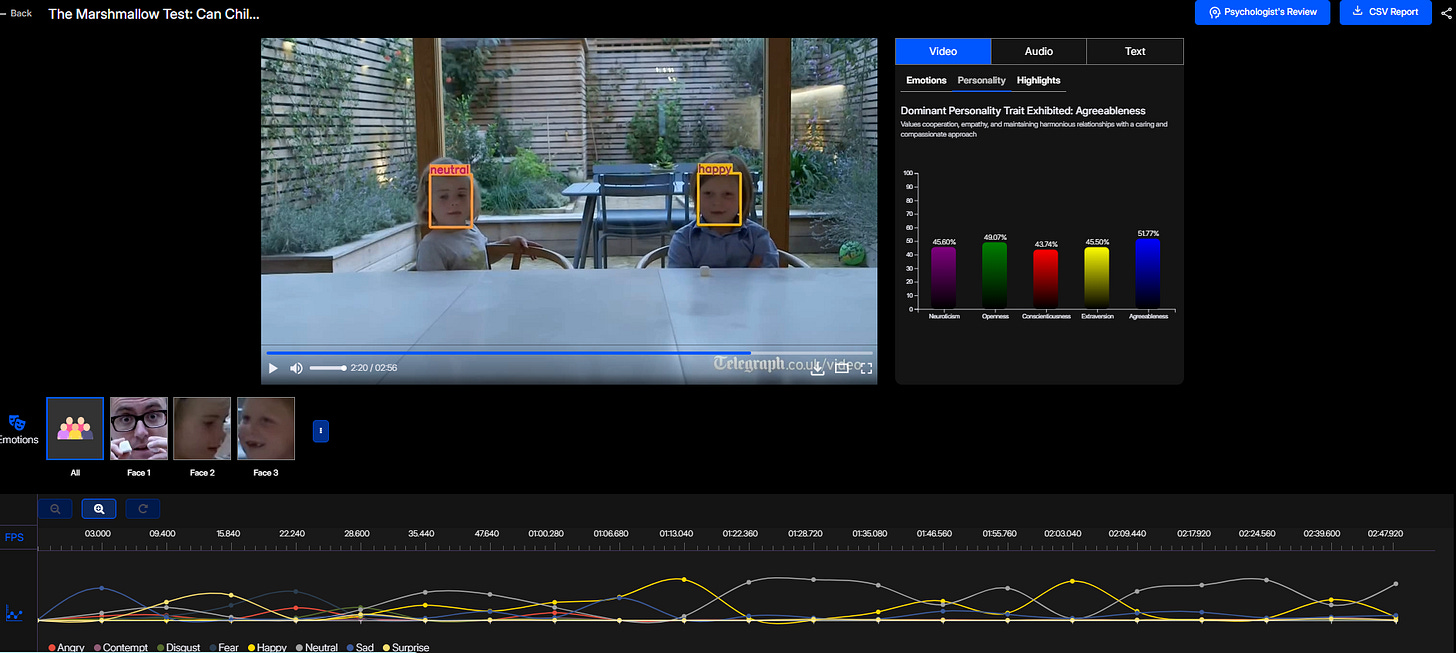
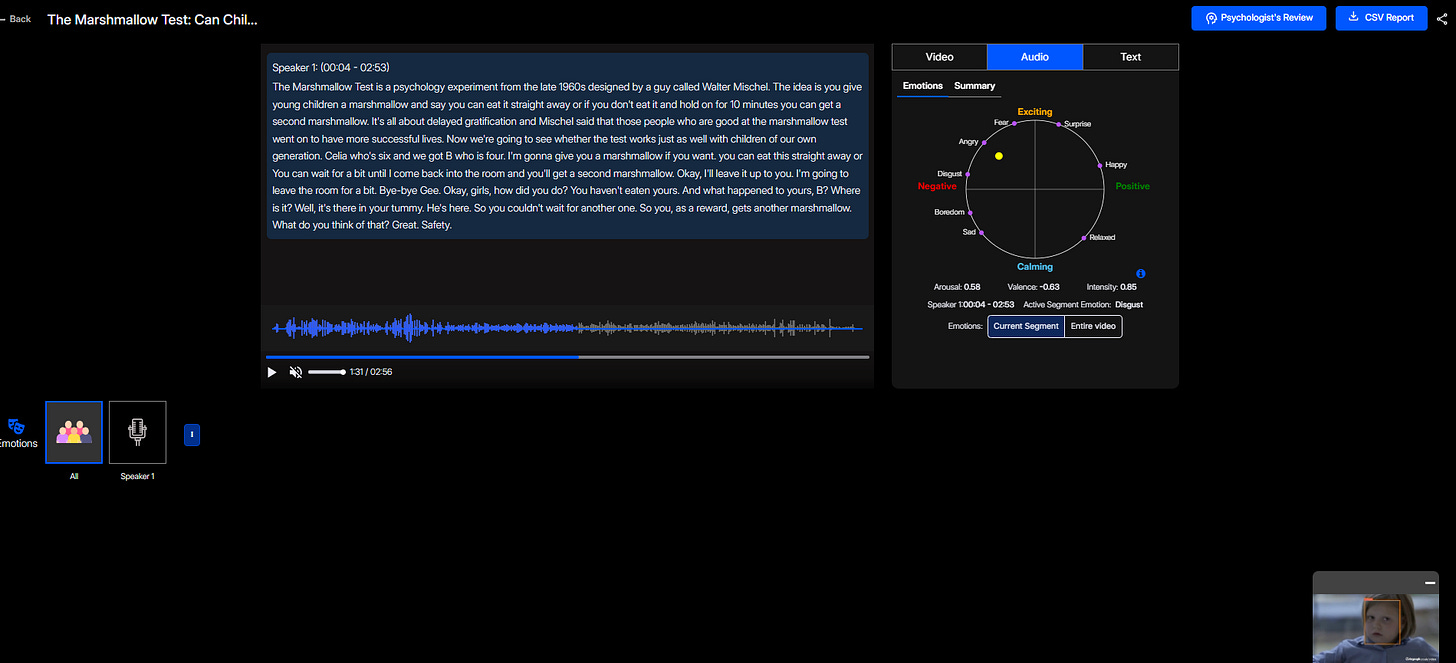
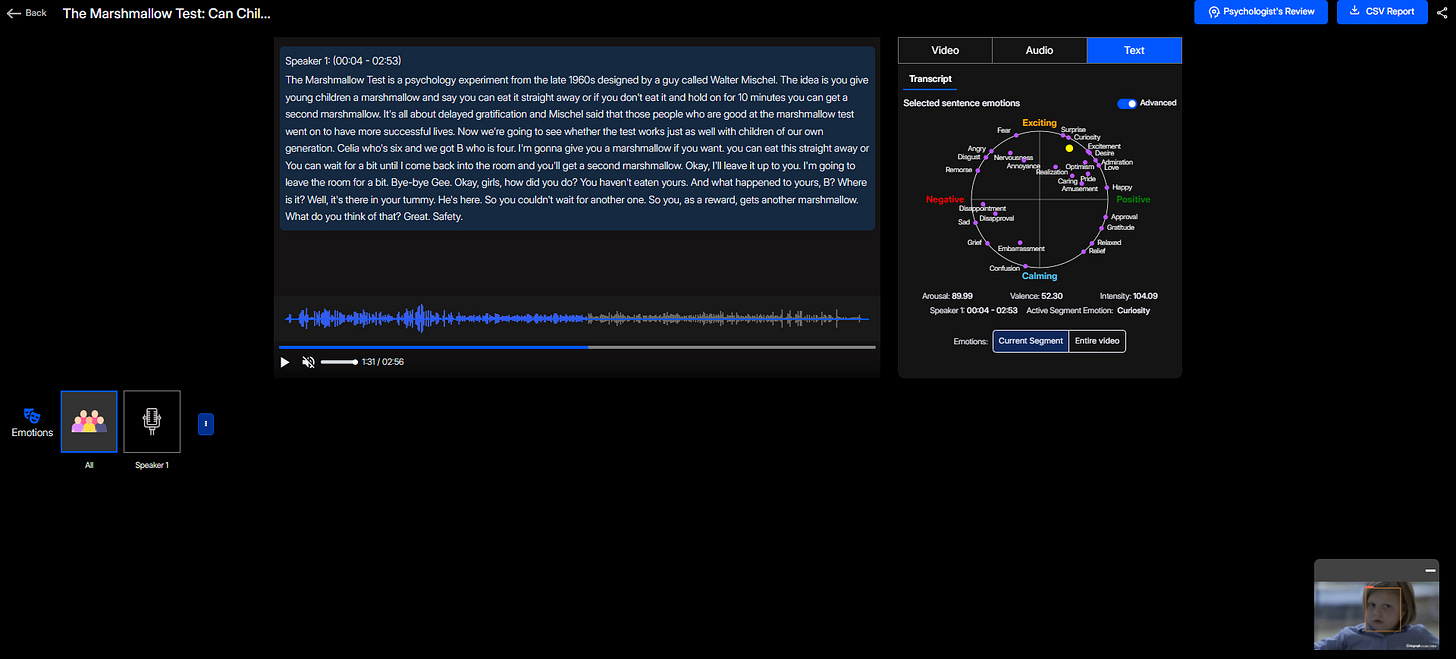
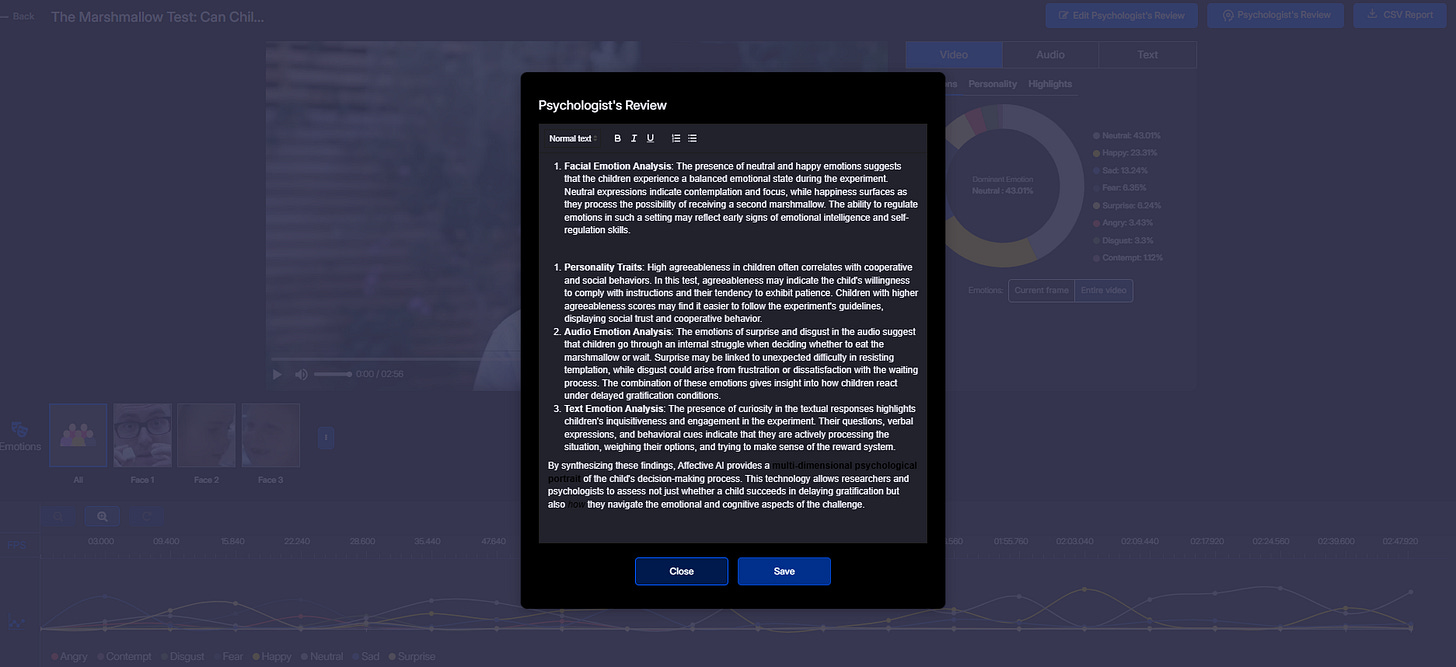
By integrating Affective AI into the analysis of this experiment, we gain more nuanced insights into children's emotional responses. Consider this video of a modern iteration of the Marshmallow Test: Imentiv AI Analysis. The AI findings for this video include:
Facial Emotion: Neutral and happy, indicating a mix of composure and amusement.
Personality Traits: High agreeableness, showing cooperation and warmth.
Audio Emotion: Surprise and disgust, reflecting emotional fluctuations during decision-making.
Text Emotion: Curiosity, suggesting an inquisitive approach to the experiment.
Detailed Psychological Analysis
The psychological implications of these findings reveal critical insights into children's cognitive and emotional processes during the experiment:
Facial Emotion Analysis: The presence of neutral and happy emotions suggests that the children experience a balanced emotional state during the experiment. Neutral expressions indicate contemplation and focus, while happiness surfaces as they process the possibility of receiving a second marshmallow. The ability to regulate emotions in such a setting may reflect early signs of emotional intelligence and self-regulation skills
Personality Traits: High agreeableness in children often correlates with cooperative and social behaviors. In this test, agreeableness may indicate the child's willingness to comply with instructions and their tendency to exhibit patience. Children with higher agreeableness scores may find it easier to follow the experiment's guidelines, displaying social trust and cooperative behavior.
Audio Emotion Analysis: The emotions of surprise and disgust in the audio suggest that children go through an internal struggle when deciding whether to eat the marshmallow or wait. Surprise may be linked to unexpected difficulty in resisting temptation, while disgust could arise from frustration or dissatisfaction with the waiting process. The combination of these emotions gives insight into how children react under delayed gratification conditions.
Text Emotion Analysis: The presence of curiosity in the textual responses highlights children's inquisitiveness and engagement in the experiment. Their questions, verbal expressions, and behavioral cues indicate that they are actively processing the situation, weighing their options, and trying to make sense of the reward system.
By synthesizing these findings, Affective AI provides a multi-dimensional psychological portrait of the child's decision-making process. This technology allows researchers and psychologists to assess not just whether a child succeeds in delaying gratification but also how they navigate the emotional and cognitive aspects of the challenge.
The Role of Imentiv AI in Enhancing Psychological Research
Imentiv AI is at the forefront of Emotion AI technology, providing comprehensive emotional analysis across video, image, audio, and text. With psychologists on board, Imentiv AI ensures that AI-driven insights are validated by psychological expertise. This synergy allows for:
Enhanced Experimentation: Automating data collection and analysis to generate objective insights.
Scalability: Enabling large-scale studies with rapid processing capabilities.
Detailed Psychological Assessments: Combining AI precision with human interpretation for deeper, research-backed findings.
Conclusion
The integration of psychological experiments with Affective AI is transforming the landscape of emotion research. By leveraging AI's ability to process video, image, audio, and text, researchers can unlock deeper insights into human emotions. The Marshmallow Test is just one example where AI-driven analysis enhances our understanding of behavioral responses. With platforms like Imentiv AI, researchers and psychologists can now access detailed, multi-modal emotional assessments, pushing the boundaries of psychological science into a new era of AI-powered discovery.
By integrating AI with traditional psychological methods, we are opening new possibilities for analyzing and interpreting human emotions in ways that were previously unattainable. The fusion of technology and psychology is not only enhancing research but also paving the way for a more profound understanding of the human mind.
To dive deeper into the fascinating world of emotion recognition AI and its applications, read more here: https://imentiv.ai/blog/understanding-emotion-ai-applications-benefits-and-limitations/
Note: Mental health conditions are serious concerns that require professional attention. While Emotion AI tools can offer valuable insights into emotional patterns, they are support elements intended to aid in understanding and assessment. These tools should be used under the guidance of licensed therapists or other mental health professionals to ensure effective and safe application in treatment.